This blog post explores the comparison between blast proof windows and standard windows. It delves into the intricacies of their design, construction, and functionality, and the role they play in providing safety and security in various settings, from residential spaces to commercial and industrial buildings.
Understanding the Basics: What are Blast Proof Windows?
Blast proof windows, also known as blast-resistant windows, are specially designed to withstand the impact of explosions and mitigate the damage caused by blast waves. These windows are constructed using advanced materials and engineering techniques to provide enhanced protection against high-pressure forces. Unlike standard windows, blast-proof windows are tested and certified to meet specific safety standards, making them a crucial component in buildings located in high-risk areas or sensitive facilities.
One key feature of blast-proof windows is their ability to prevent the penetration of glass shards and debris into the building during an explosion, thus reducing the risk of injuries to occupants. These windows are engineered to absorb and dissipate the energy generated by a blast, helping to minimize structural damage and maintain the integrity of the building envelope. In addition to protecting against external threats, blast-proof windows also offer enhanced security benefits, as they are more resistant to forced entry and intrusions.
The design of blast-resistant windows typically involves multiple layers of glass, laminated interlayers, and reinforced frames to enhance their strength and durability. These windows are subjected to rigorous testing procedures, including pressure impulse tests, to ensure their ability to withstand various blast scenarios. While blast-proof windows may initially cost more than standard windows, the long-term benefits in terms of safety, security, and potential savings on insurance premiums make them a valuable investment for many property owners.
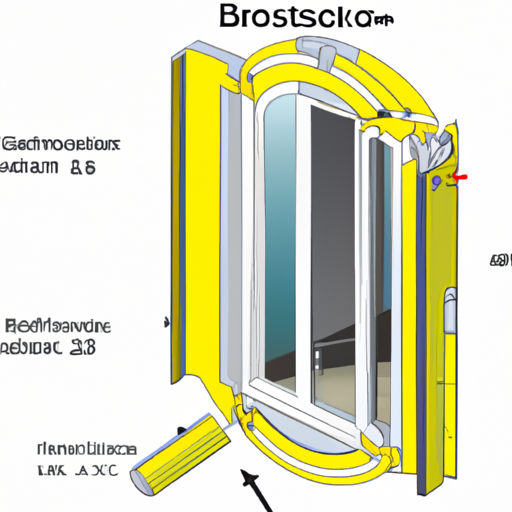
An illustration showing the cross-section of a blast proof window
How Do Blast Proof Windows Work? The Science Behind the Safety
Blast-proof windows operate on the principles of energy absorption and dissipation to withstand the impact of explosions. They are designed to absorb the shock waves generated by a blast and prevent the transfer of excessive pressure into the building. One of the key components of blast-resistant windows is the use of multiple layers of glass with varying thicknesses and properties. These layers work together to distribute the force of the blast over a larger surface area, reducing the risk of glass breakage and structural failure.
In addition to the glass layers, blast-proof windows often incorporate laminated interlayers made of materials such as polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). These interlayers serve to hold the glass panes together in the event of breakage, preventing shards from becoming projectiles and minimizing the risk of injuries. The combination of multiple glass layers and interlayers enhances the overall strength and resilience of the window system, making it more resistant to blast forces.
"Are Blast Proof Windows Really Worth the Investment?": Evaluating the Costs and Benefits
"Are Blast Proof Windows Really Worth the Investment?": Evaluating the Costs and Benefits:
When considering the implementation of blast-proof windows, it is essential to weigh the costs against the potential benefits they offer. While the initial investment in blast-resistant windows may be higher compared to standard windows, the long-term advantages in terms of safety and protection can outweigh the upfront expenses. The enhanced security provided by blast-proof windows can significantly reduce the risk of property damage and personal injury in the event of an explosion. This can result in potential cost savings by minimizing the need for repairs and replacements, as well as reducing liability concerns for building owners.
A graphical representation of cost-benefit analysis between blast proof and standard windows
Blast Proof vs. Standard Windows: A Comparative Analysis
When comparing blast-proof windows to standard windows, it is crucial to consider various factors that differentiate the two in terms of safety, durability, and performance. Blast-proof windows are specifically designed and tested to withstand high-impact forces, such as those generated by explosions, making them ideal for high-risk environments where security is a top priority. Standard windows, on the other hand, are not engineered to provide the same level of protection against such extreme events.
One key difference between blast-proof and standard windows is the materials used in their construction. Blast-proof windows are typically made with reinforced glass and framing materials that are specifically chosen for their ability to absorb and dissipate blast energy effectively. In contrast, standard windows may not have the same level of impact resistance, making them more vulnerable to damage in case of an explosion.
Another important aspect to consider is the testing and certification process that blast-proof windows undergo to ensure their compliance with safety standards. These windows are rigorously tested to simulate blast conditions and verify their ability to withstand the forces generated by explosions. Standard windows do not undergo the same level of testing and may not offer the same level of protection in hazardous situations.
In conclusion, while standard windows may be sufficient for regular use in most residential and commercial buildings, the value of blast proof windows cannot be underestimated. They offer enhanced protection, durability, and peace of mind, especially in regions prone to natural disasters or in high-security buildings. The choice between the two ultimately depends on the specific needs and safety requirements of the user.
